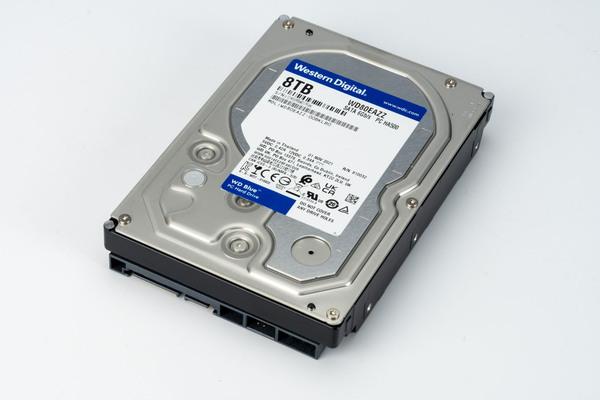
8TB model of WD Blue is recommended for large capacity HDD! The reason is the reliability of the CMR recording method
Thank you for waiting. I may have kept you waiting too long.
While the world is shifting toward SSDs, when it comes to low-cost, high-capacity storage for data storage, HDDs are still the clear winner. standing in
The storage manufacturer Western Digital has a series of HDDs such as ``WD Blue'' for general use, ``WD Red'' for NAS, ``WD Purple'' for surveillance systems, and ``WD_BLACK'' for game users. HDD is prepared.
This time, the 8TB model, which had been available only in high-end series such as "WD Red", has finally appeared in the general "WD Blue" series. Since the 6TB model has been the only model so far, it is now possible to use storage with more capacity.
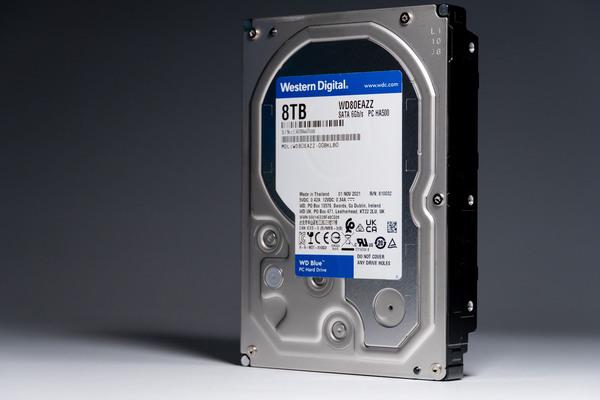
8TB model "WD80EAZZ" appeared from the WD Blue series. Rotation speed is 5640rpm
This is quite good news. If you try to secure a data storage location by building it in your own or desktop machine, you can add one or two at most. If the capacity of one drive is too small, it will not be possible to store a lot of data.
In addition, since a 3.5 inch drive cannot be built into a notebook PC, it will be used as an external drive from the beginning. In that case, it is almost impossible to connect more than one, so it is better to have a large capacity with one unit. Purchasing a model with as large a capacity as possible is the key to choosing an HDD.

The recording method adopts the conventional CMR, what is the difference from SMR?
However, this is a bit of a maniac story, but the 8TB model this time is not the SMR recording method that is often used these days, but the higher-end model of the "WD Red" series and the more reliable "WD Red Plus". series, the conventional CMR recording method is used.
In the first place, let's briefly explain what SMR and CMR are. HDDs write data by magnetizing metal discs coated with magnetic material, known as platters, using a magnetic head. Data is stored in areas called tracks arranged concentrically in units called sectors, but the difference lies in the recording method.
SMR (Shingled Magnetic Recording) is a method that aims to increase the recording density and increase the capacity at a low cost, and is the current mainstream in which tracks are partially overlapped and multiple tracks are written as blocks at once. On the other hand, CMR (Conventional Magnetic Recording) is an orthodox method that has been used for a long time.
SMR (image right) is a method of writing multiple tracks at once as blocks by overlapping tracks. It is a technology that can increase the recording density and aim for a large capacity at a low cost (image extracted from the Western Digital website)
The difference between the two is the case of partial rewriting. In CMR, only specific data can be simply rewritten, but in the case of SMR, as the tracks overlap, only specific data cannot be rewritten, and even the data written adjacently is erased.
In the case of SMR, since the tracks overlap, it is not possible to rewrite only specific data, and all adjacent data is rewritten. In other words, in the unlikely event that the data is corrupted, the adjacent data will also disappear (image taken from Western Digital's blog)
For this reason, with the SMR recording method, it is necessary to have a cache memory, move it temporarily in block units, format it once to rewrite it, and then restore it. This practice is similar for SSDs, but this process can be good or bad for random write performance.
In the case of CMR, there is no such process and stable writing is performed, and many users feel more secure with CMR.
In the WD Blue series, 500GB and 1TB were CMR, but 2TB, 3TB, 4TB, and 6TB have adopted SMR. With the revival of CMR in this 8TB, a large-capacity, more reliable and secure HDD for general use was born.


![10th generation Core i5 equipped 9.5h drive mobile notebook is on sale at 50,000 yen level [Cool by Evo Book] 10th generation Core i5 equipped 9.5h drive mobile notebook is on sale at 50,000 yen level [Cool by Evo Book]](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/9/4a18d0792cae58836b71b9f591325261_0.jpeg)




![[Amazon time sale in progress! ] 64GB microSD card of 1,266 yen and wireless earphone with noise canceling function of 52% off, etc. [Amazon time sale in progress! ] 64GB microSD card of 1,266 yen and wireless earphone with noise canceling function of 52% off, etc.](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/9/c88341f90bab7fe3ce1dc78d8bd6b02d_0.jpeg)
